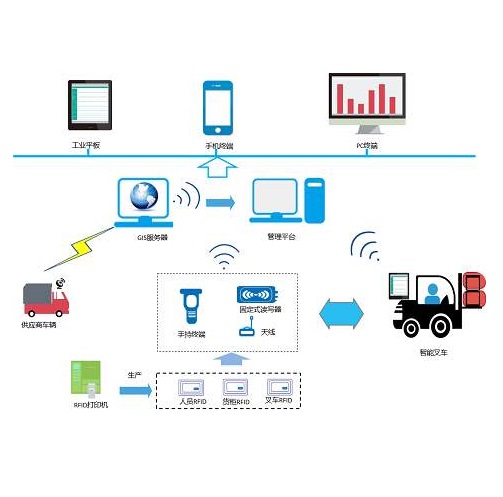
The Transmission RFID weighing system transmits data to the monitoring computer in real time, and the monitoring computer can also call the data in the host database at any time. Weighing system plays a great role in improving the efficiency of cargo transportation and handling, making the business management mode orderly, standardized and scientific, thus improving the management level and reducing the cost. As the information (front-end) collection tool of weighing system, long-distance RFID technology can significantly improve the collection speed, and effectively prevent human fraud from bringing economic losses to enterprises and institutions through automatic identification and disassembly prevention measures.
 020-34563445
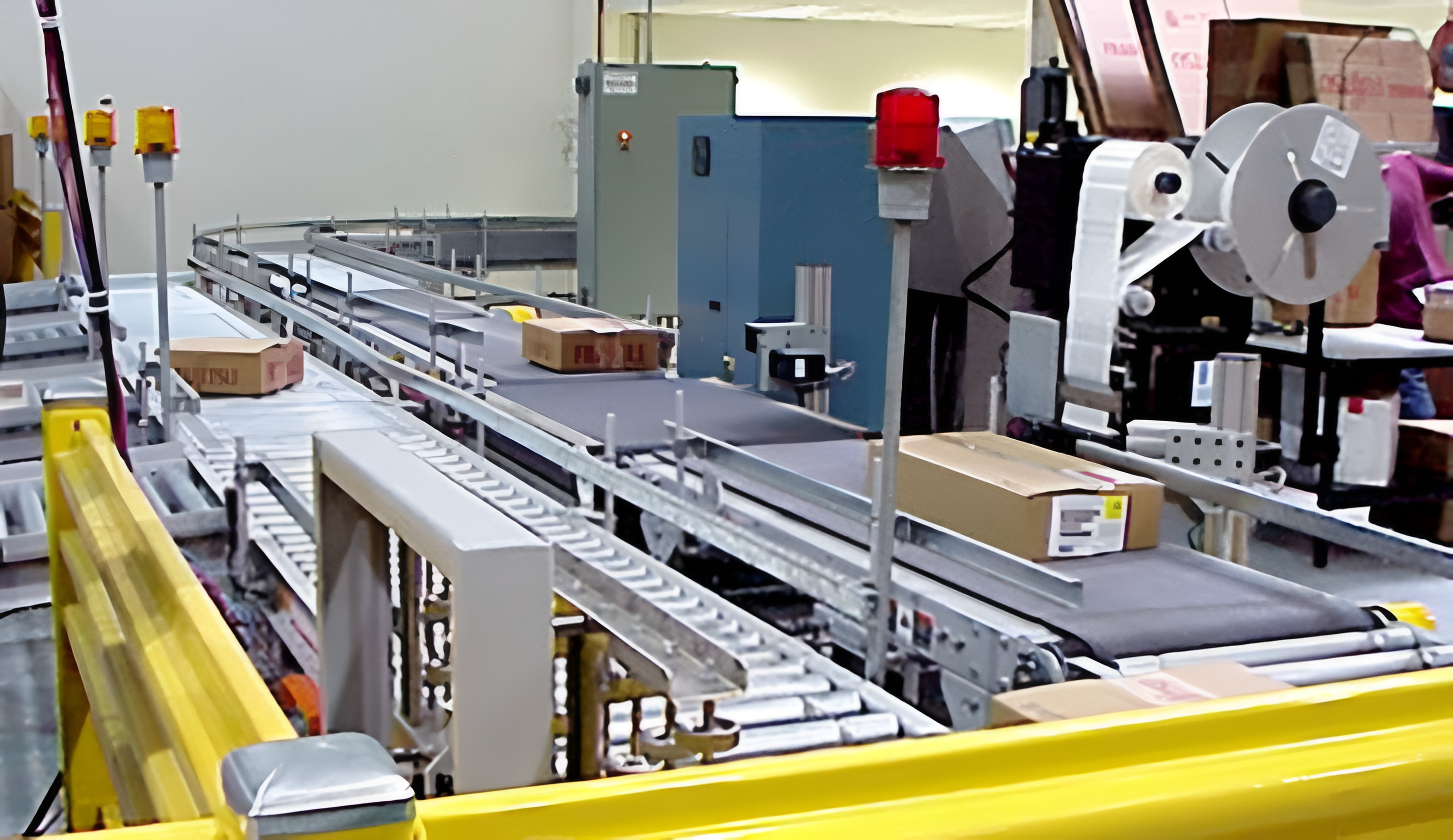
020-34563445The airport transmission RFID Weighing system consists of the departure subsystem and the arrival subsystem. The departure subsystem includes conveyors, baggage identifiers, automatic sorters, horizontal diverters, vertical diverters, electrical control equipment and network connection equipment, etc. Luggage is processed at the check-in counter and enters the collection conveyor. It is conveyed by the ordinary conveyor and tracked and identified by the RFID system. The luggage is then transported to the designated automatic Sorting machine for precise sorting through the primary sorting by the horizontal and vertical dividers. The automatic sorting machine then conveys the luggage to the departure carousel of the corresponding flight for packing according to the flight classification. The DCV baggage handling system, also known as the intelligent destination coding trolley system, mainly undertakes the task of high-speed transportation of passengers' luggage. The system's sorting has multiple redundant paths, and the luggage sorting can run according to the optimal path, reaching the corresponding sorting destination in as fast as 2 minutes, minimizing the luggage consignment delivery time to the greatest extent.
The luggage system is 32 kilometers long (14 kilometers for the belt system and 18 kilometers for the pallet system), and it has approximately 4,800 small vehicles. This luggage system is equipped with 11 check-in islands, 22 collection and conveyor lines, 42 departure carousels, 21 arrival carousels, 2 early arrival systems that can accommodate a total of 4,000 pieces of luggage, 2 transfer systems, 11 three-level security check opening rooms, and 2 sets of transfer and re-check-in systems. The system is designed with an outbound luggage processing capacity of 15,400 pieces per hour and an inbound luggage processing capacity of 7,900 pieces per hour, capable of handling a passenger flow of 45 million years.
At the same time, the luggage system is equipped with an RFID electronic tag identification system, on which the personal information of passengers, departure, arrival, flight number and other information are recorded. Through RFID readers, the information of passengers' luggage can be read at high speed, solving problems such as barcode labels being blocked or multiple barcodes existing in suitcases, and achieving efficient tracking and sorting. The Early Arrival system is an independent sorting system that adopts a pallet storage mode and can accommodate up to 4,000 items. It can also precisely and efficiently retrieve single or multiple pieces of early arrival luggage according to the system Settings, enhancing the sorting function of the system.
The new terminal building has two check-in islands, both equipped with fully self-service baggage check-in facilities, which are evenly distributed for use on both domestic and international sides. Passengers using domestic self-service check-in equipment need to check in and print luggage tags by themselves in the self-service check-in equipment first. Only after the luggage is tied with the tags can it be checked in by self-service. International self-service can complete the printing of luggage barcode labels in one device, and then bind the luggage barcode under the guidance of the device to complete the check-in process. If luggage needs to be inspected for security reasons, the screen will provide corresponding prompts to guide passengers to the designated luggage opening room for inspection.
Baggage handling system process
The check-in counter is equipped with a three-stage check-in conveyor. The first section includes a scale conveyor belt with load-bearing and weighing functions, as well as a labeling function. The second section is used for the conveying control of the countertop X-ray security inspection machine. The third section is responsible for delivering the waiting luggage to the collection belt.
Disposable RFID luggage tags will be used at the check-in counter. In addition to the luggage code, when printing, the RFID chip in the label will also be simultaneously written with user-defined additional information other than the IATA barcode. Irregularly shaped and soft-packed luggage that is prone to rolling or slipping on the conveyor belt surface should first be loaded into empty luggage baskets before being conveyed.
The second section of the check-in conveyor, also known as the countertop security inspection machine conveyor, is controlled by the luggage handling system and needs to achieve self-locking and interlocking functions. That is, before the result of the luggage waiting for inspection on the channel is obtained, the security inspection machine cannot enter the next piece of luggage in this channel, and the dual-channel security inspection machine can only allow one piece of luggage to enter at the same time.
After the luggage passes through the security inspection machine, the security inspection machine will inspect the items inside the luggage. After the inspection is completed, the luggage will stay on the third check-in line to wait for the safety result of the luggage. The luggage that passes safely as a result will be introduced into the collection conveyor line. These luggage will be tracked to ensure they are always in a safe state and then loaded onto DCV pallets and conveyed to the departure loading turntable at the destination.
There is a time limit for luggage waiting for security check interpretation, which is defaulted to 2 minutes. If the time limit is exceeded, the status will be sent to the luggage security check system, and the luggage will be sent to the luggage opening room for processing. The luggage that has been rejected by security checks is also introduced into the collection conveyor line and diverted by the diverter to the checked luggage opening room at the end of the check-in island for opening and inspection. Luggage that requires further inspection is also diverted to the luggage opening room for processing. The luggage will be further inspected by security personnel to ensure safety before entering the luggage system. The luggage that passes the inspection through this process will be re-scanned for the label barcode and returned to the luggage handling system. After the luggage is imported into the check-in collection belt and before it reaches the luggage diversion point in the opening room, the luggage handling system tracks the luggage through a PLC traceability algorithm.
Before opening the luggage compartment, there is a luggage tag reading device at the diversion point. It reads the RFID tags of the luggage and receives the interpretation results sent by the communication server of the luggage security inspection system. By comparing the execution signals of the on-site security inspection machine with the PLC tracking of the above-mentioned luggage handling system, it is determined whether the luggage should be diverted to the opening compartment. Luggage that is tracked and lost at the luggage opening room diversion point will be sent back to the luggage opening room. The entrance conveyor line of the luggage opening room is equipped with a rejection indicator light at a prominent position to distinguish and display the status of luggage entering the luggage opening room, including tracking loss and various rejection statuses, etc. The indicator light is accompanied by relevant types of identification information explanations. Before the luggage is loaded onto the pallet, all the information within the tag will be read through the barcode /RFID composite ATR, and ultimately associated and bound with the pallet information of the DCV to perform conveying and sorting.
Highly intelligent logistics data system
The intelligent data management system tracks in real time every link of passengers' luggage transportation, sorting, packing, loading and unloading. Passengers can query the location information of their luggage through the APP. Airports and airlines, through the big data operation system, can verify, monitor, track and search for tens of thousands of pieces of luggage in real time every day. Some domestic airports attach chips to luggage barcodes, embedding flight information, luggage information, etc. of passengers' luggage into the chips. When passengers' luggage enters the luggage system, the information is read into the luggage system through high-precision luggage identification devices (RFID), serving as the basis for tracking, conveying and sorting luggage in the luggage system. The luggage information can be read through the handheld terminals of the staff, which serves as an important basis for packing, loading, unloading and the distribution of luggage information upon arrival at the port. Meanwhile, the data information of the luggage can be shared with passengers. Passengers can track their luggage throughout the entire process by logging into the APP.
Highly reliable mechanical equipment and backup systems
The luggage handling system of civil aviation airports has high requirements for the timeliness and accuracy of luggage transportation and sorting, so it has high requirements for the mechanical equipment and devices of the luggage system, especially the reliability of the mechanical equipment and devices. The design of the processing system is unreasonable, and its reliability is low. Frequent equipment failures can lead to interruptions or low efficiency in luggage transportation and sorting, resulting in serious consequences such as delayed luggage transportation, flight delays, and passenger complaints. Moreover, when designing the luggage handling system, the backup principle of mechanical equipment and devices and other systems should be taken into consideration. The flow direction of luggage can be changed through horizontal and vertical diverters. Luggage can be sorted in a backup manner through multiple sorting machines. Multiple systems can operate independently to sort luggage. During peak luggage hours, they can also coordinate and link to sort luggage simultaneously. In case of faults, they can switch between each other to handle luggage. Thus, a redundant system backup design can be achieved.