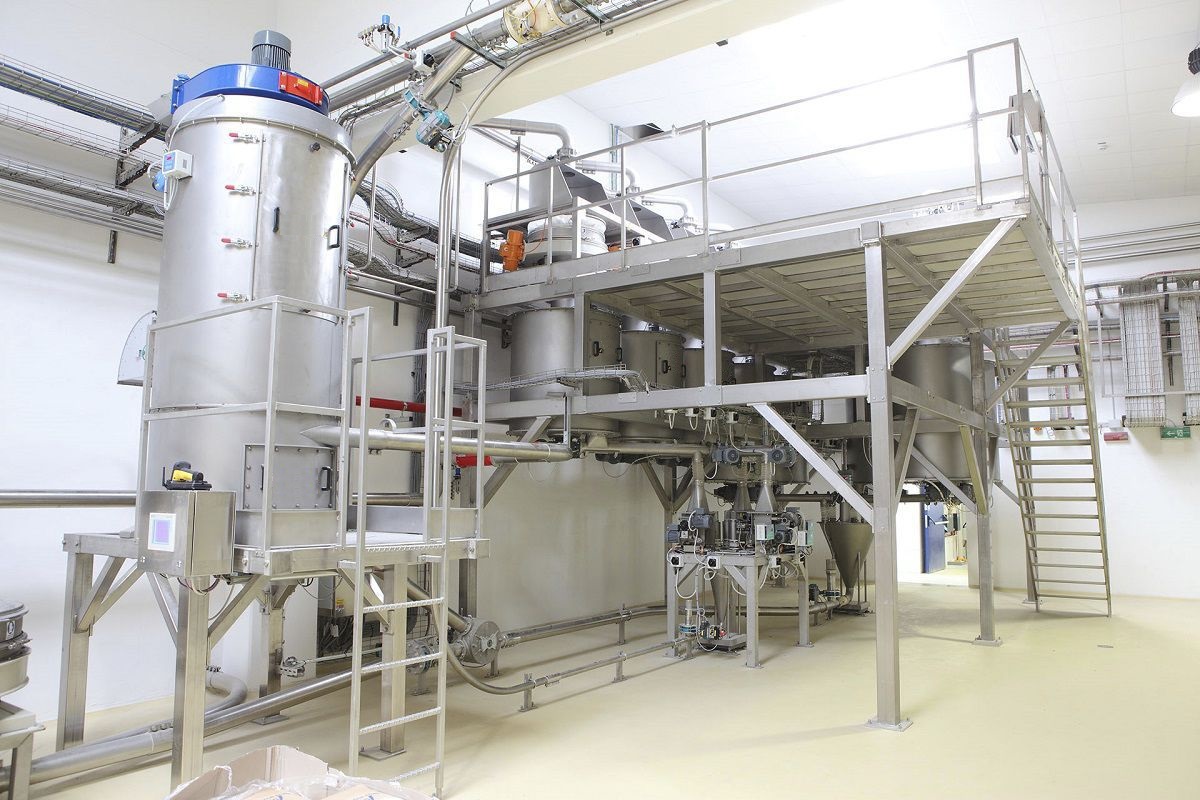
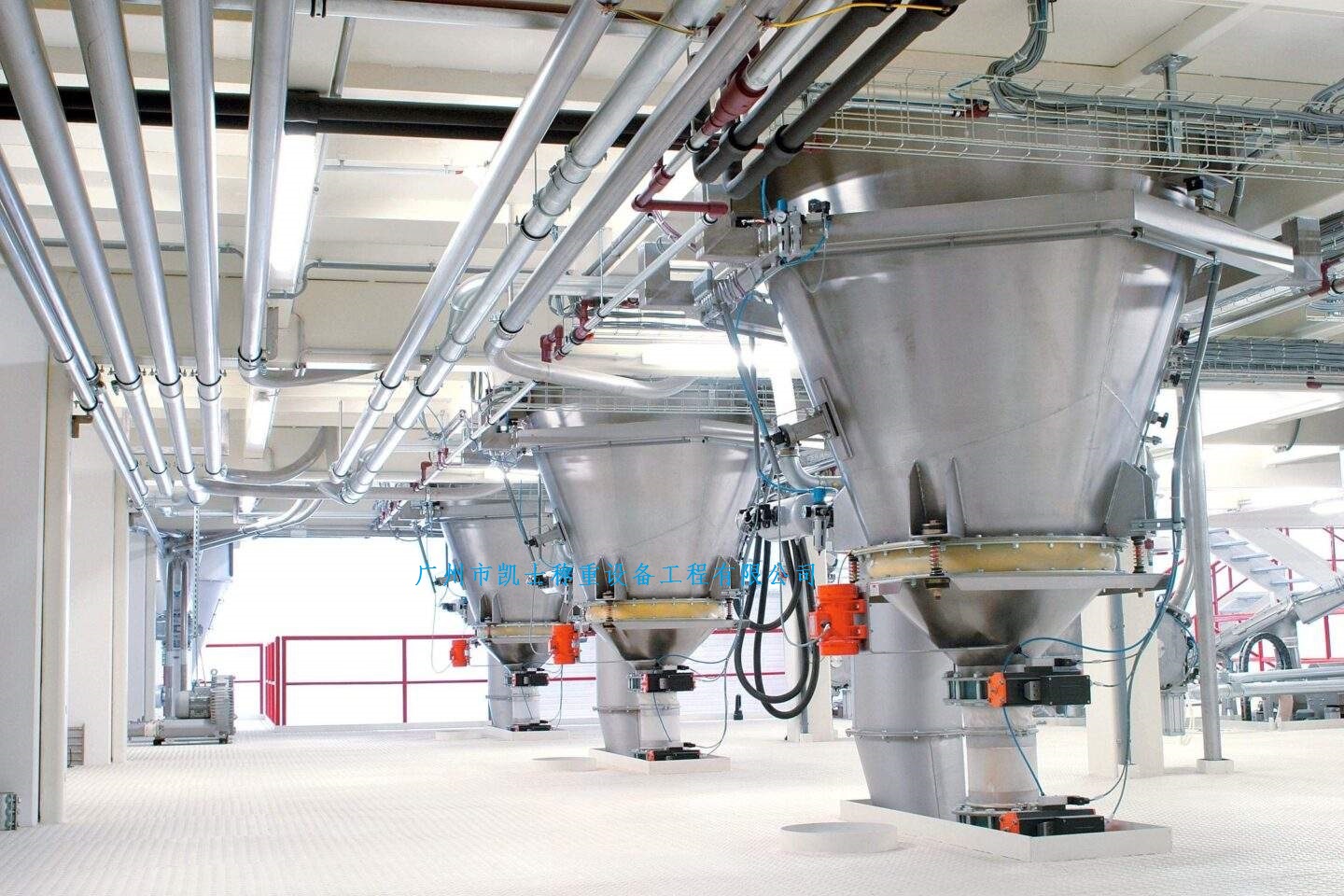
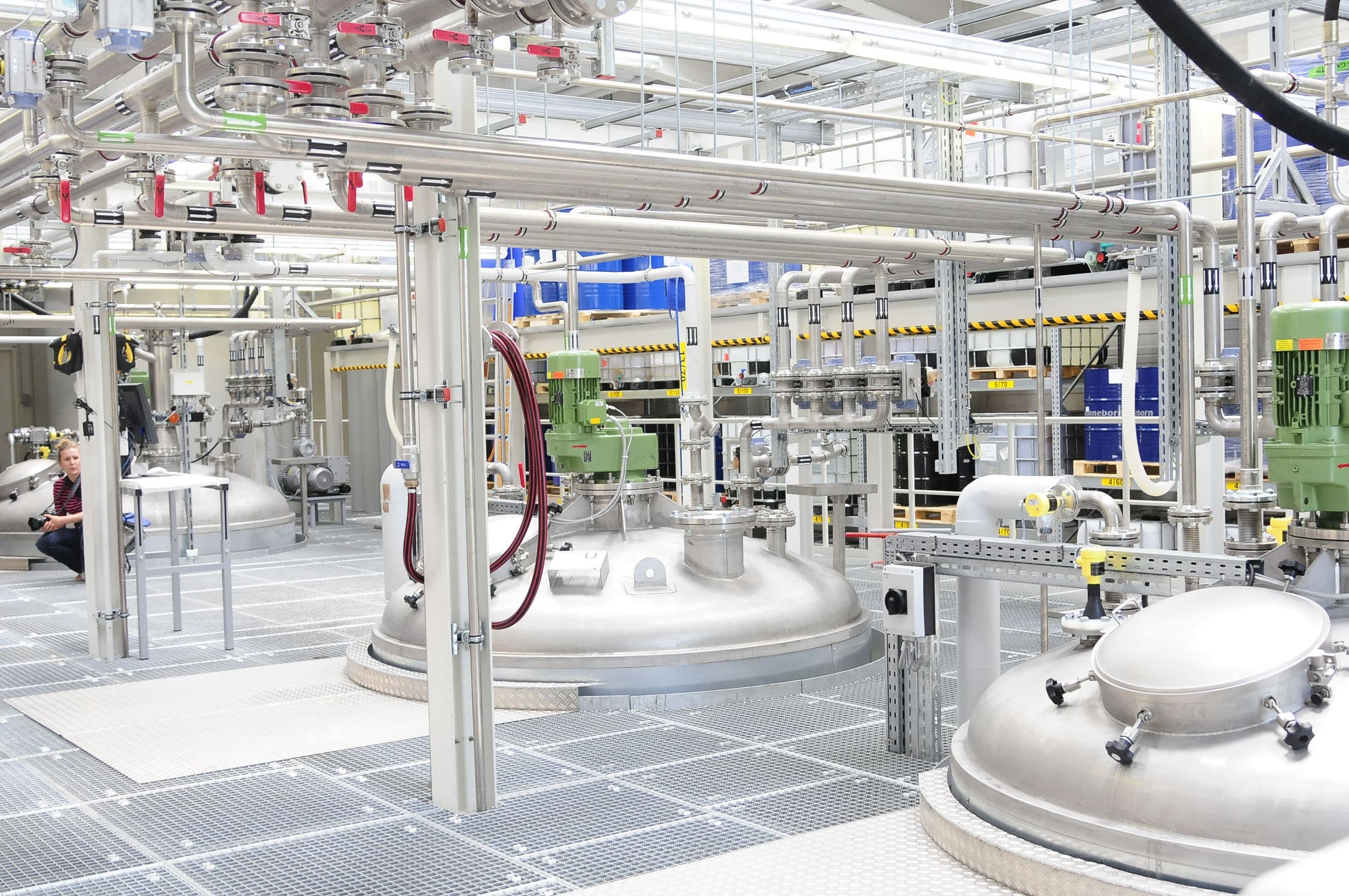
The Sealed feeding system mixes raw materials and auxiliary materials together in a certain proportion according to the production process regulations; It is a process of feeding and discharging materials according to pre-set values and errors for one or more materials. The dosing process requires no dust, can be reviewed and traceable, and minimizes the risk of contamination, cross-contamination, confusion and error during the transfer of powder materials.
 020-34563445
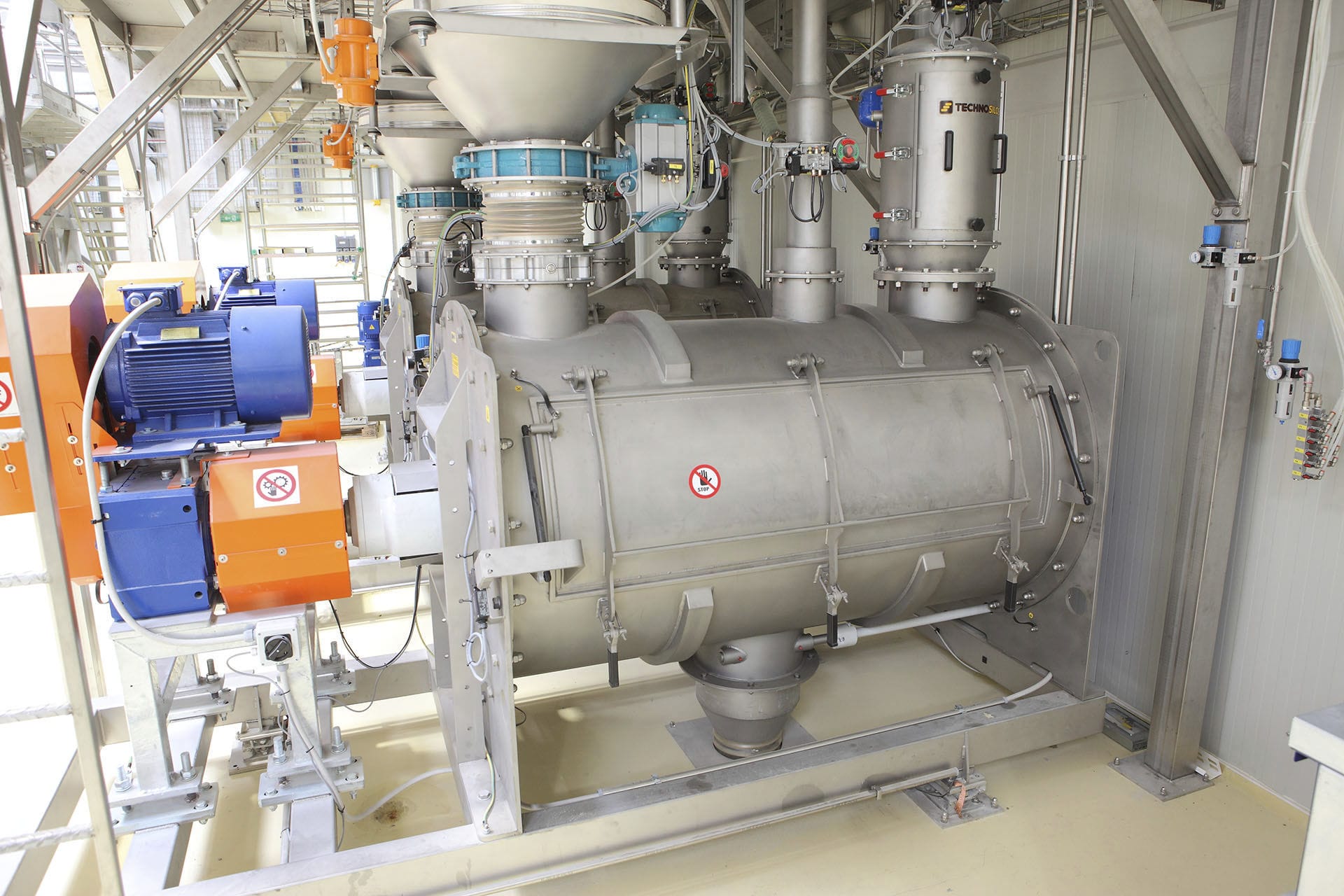
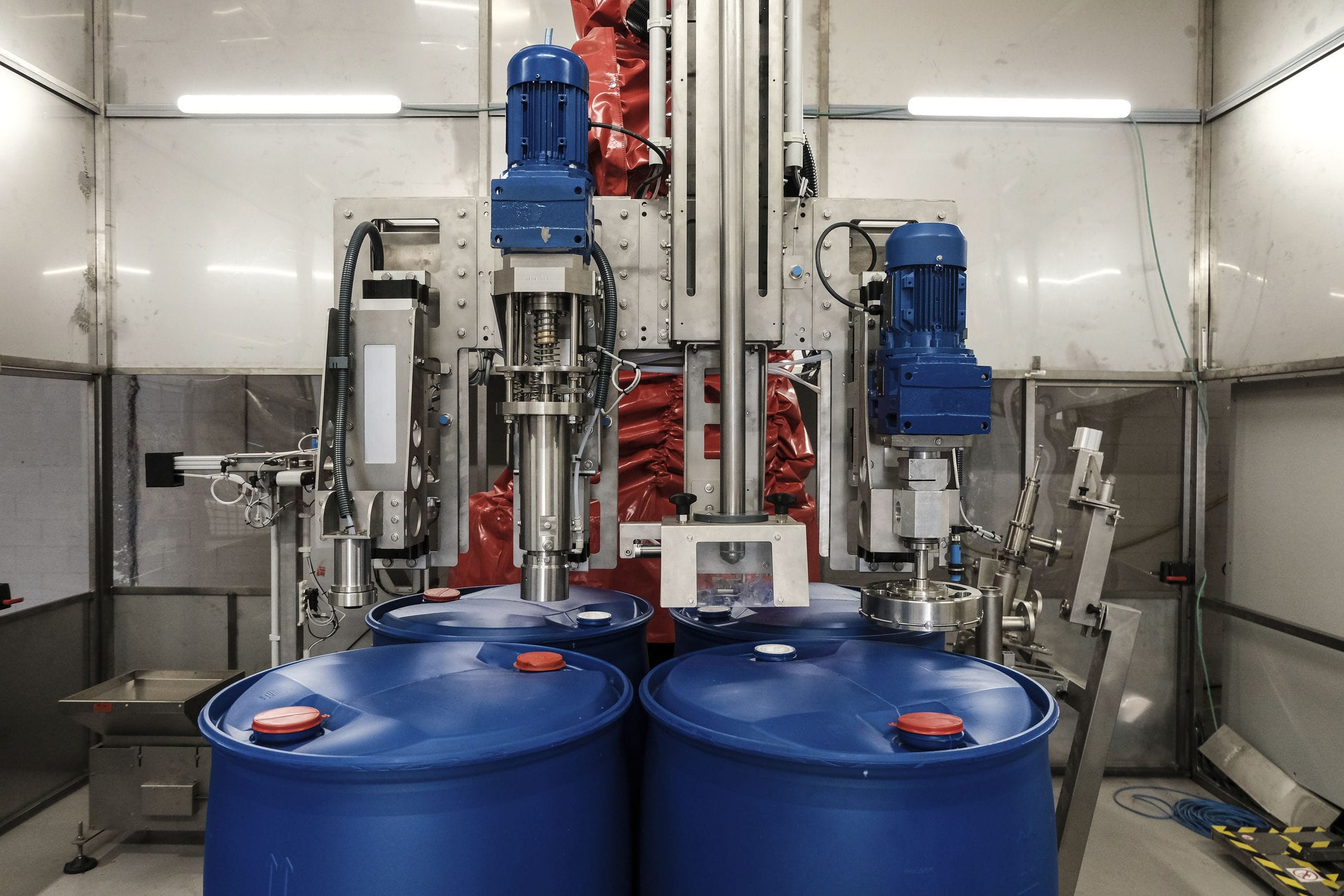
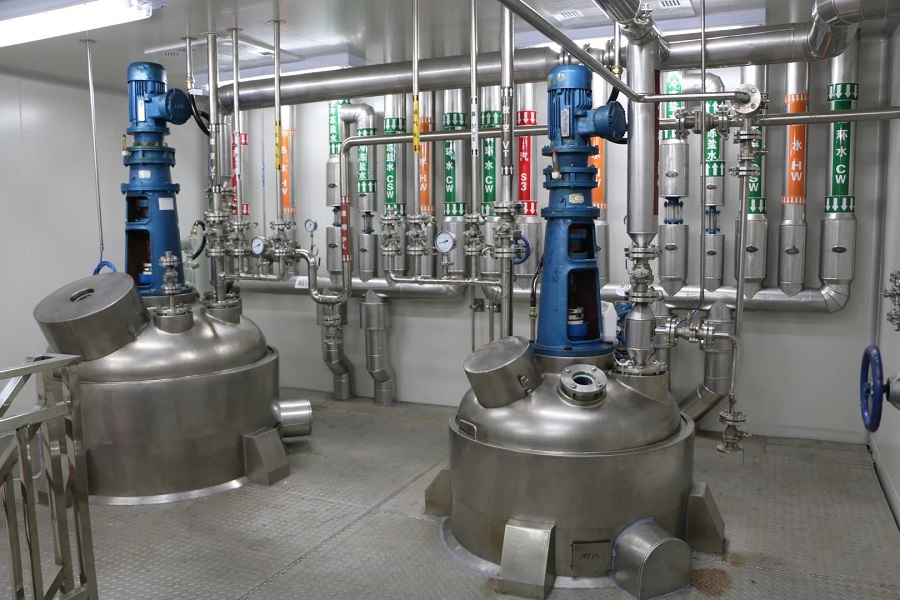
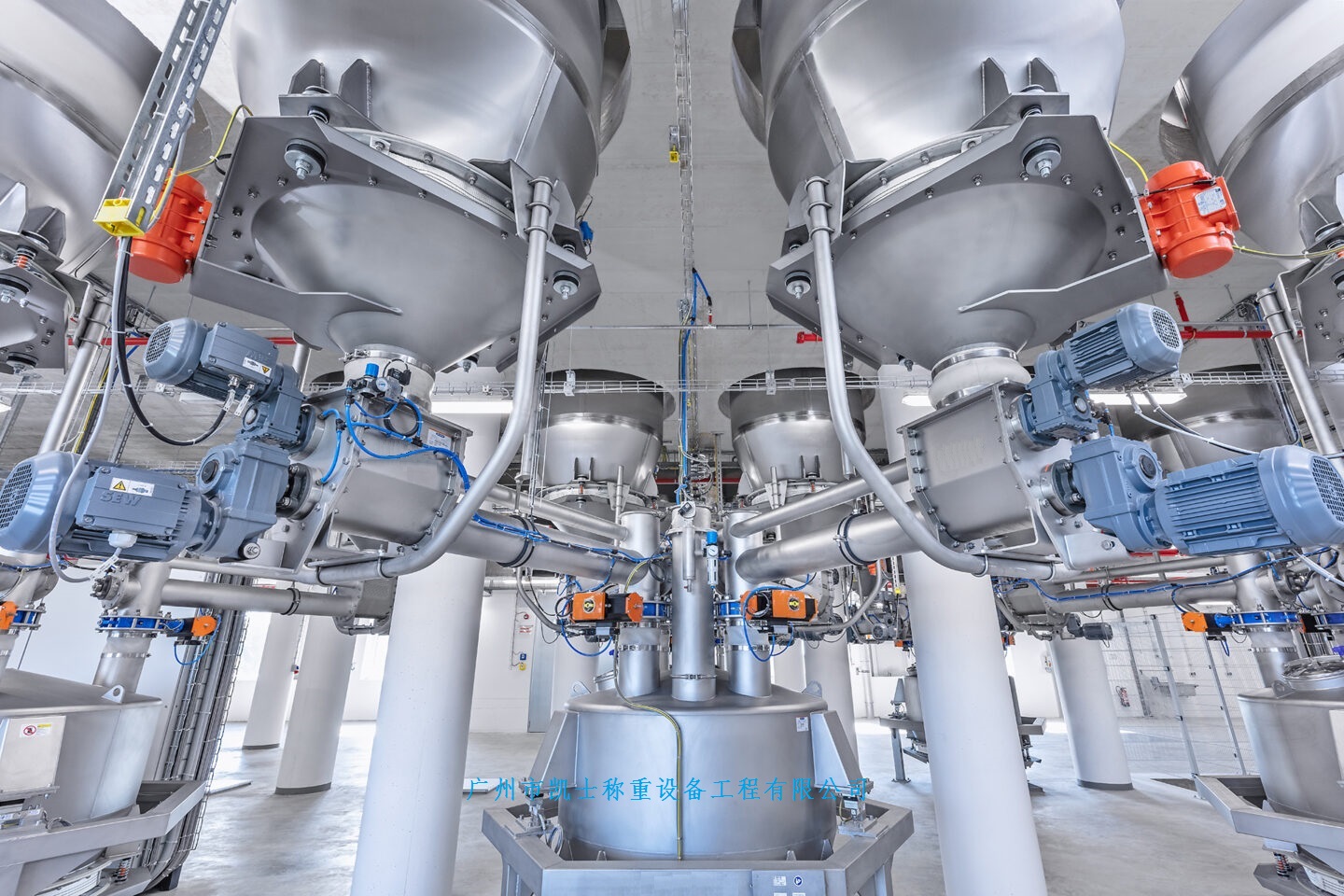
020-34563445The Sealed feeding system is a pressurized closed system with nitrogen as the conveying gas and powder as the conveying material. The material enters the hopper from the upstream section and enters the conveying line through the rotary Feeder under the hopper. The power of the system is provided by the compressor. Through the pressurized nitrogen of the compressor, the material in the pipeline under the rotary valve is sent to the target silo to complete the conveying task. The nitrogen is filtered through a filter in the upper part of the target silo and returned to the compressor population for recycling. The line where the control valve is located is a nitrogen refill line, through which the system replenished nitrogen to the system in the early stage of operation or in case of insufficient nitrogen pressure. The valve in the pipeline is a nitrogen discharge pipeline. When the pressure in the system is too high, the two valves can be opened to exhaust nitrogen into the atmosphere to reduce the system pressure. Since compressors and rotary feeders are dynamic equipment, have a certain failure rate and require regular maintenance, these equipment are configured as one use one standby.
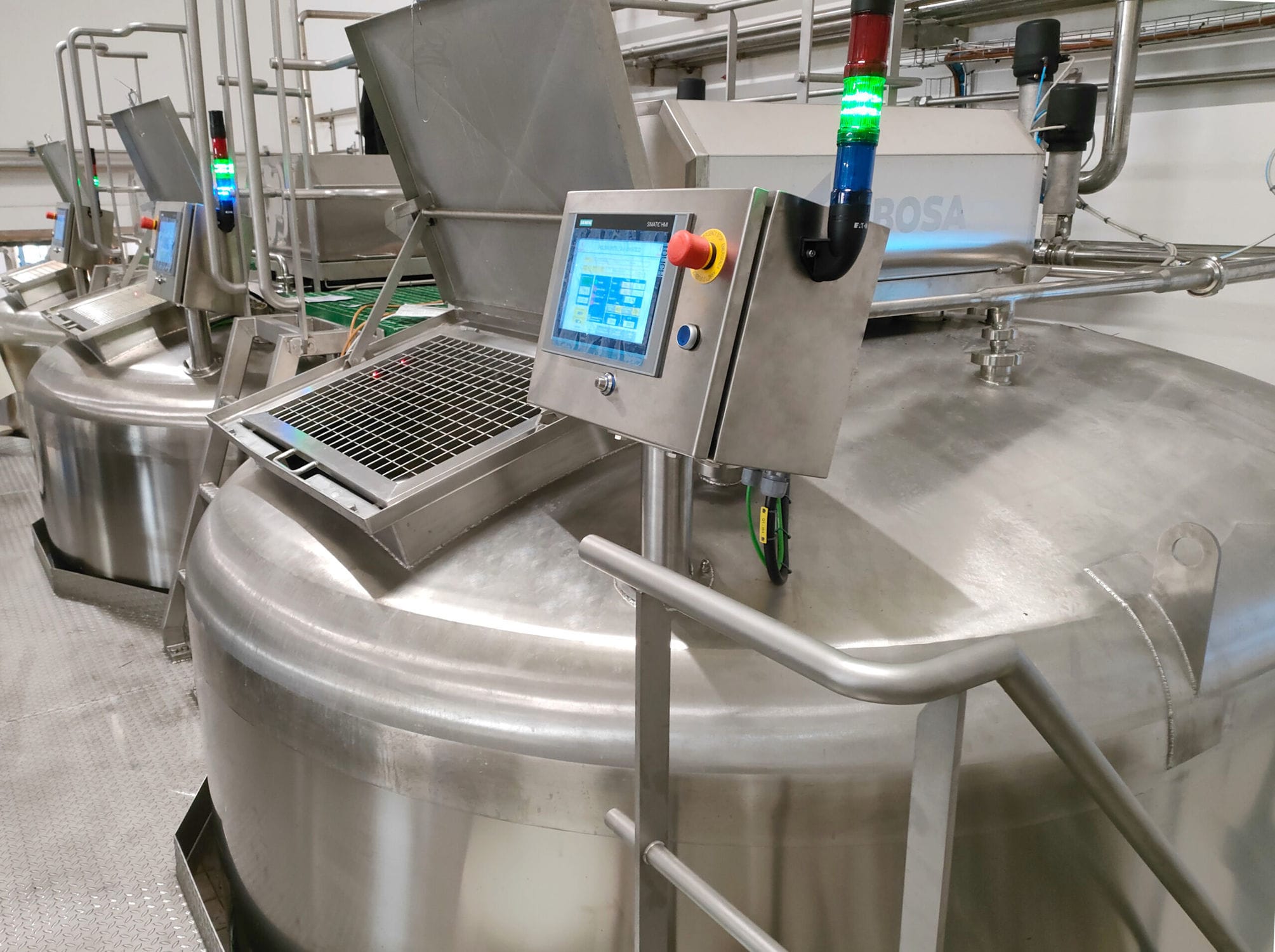
The feeding system is operated continuously, automatically and remotely under normal conditions, so it is equipped with corresponding remote control valves and metering instruments. The valve mainly adopts the butterfly valve and the three-way valve with the cylinder actuator, and realizes the remote control of the valve through the solenoid valve. The pressure transmitter and temperature transmitter are set on the compressor outlet/population and the target silo respectively for the measurement of pressure and temperature parameters. An oxygen analyzer is installed at the compressor outlet to measure the oxygen volume fraction in the system. Level switches are set at different heights on the target silo to realize level alarm function.
Before the system can be started, the entire system needs to be filled with nitrogen until the oxygen analyzer indicates that the volume fraction of oxygen is less than the specified number. This process is usually done manually. Because the material transported is a flammable medium, too high oxygen content will cause the material to catch fire in the pipeline friction. After the oxygen content index is normal, the operator selects the conveying path at the operation station in the control room, that is, the feeding hopper, the rotary feeder, the compressor and the target bin. After selection, the valve at the inlet and outlet of the selected compressor opens, the bypass valve of the compressor opens, the valve under the rotary feeder opens, the three-way valve points to the selected bin, and the nitrogen return valve opens. The above actions are done automatically by the program. At this point, the preparation for the system start-up has been completed. After the process operator issues the start-up instruction on the operation station, the start-up steps are as follows: start the compressor; Close the bypass valve, the system pre-purge a certain time; Start the rotary feeder, start conveying materials, and the system is started.