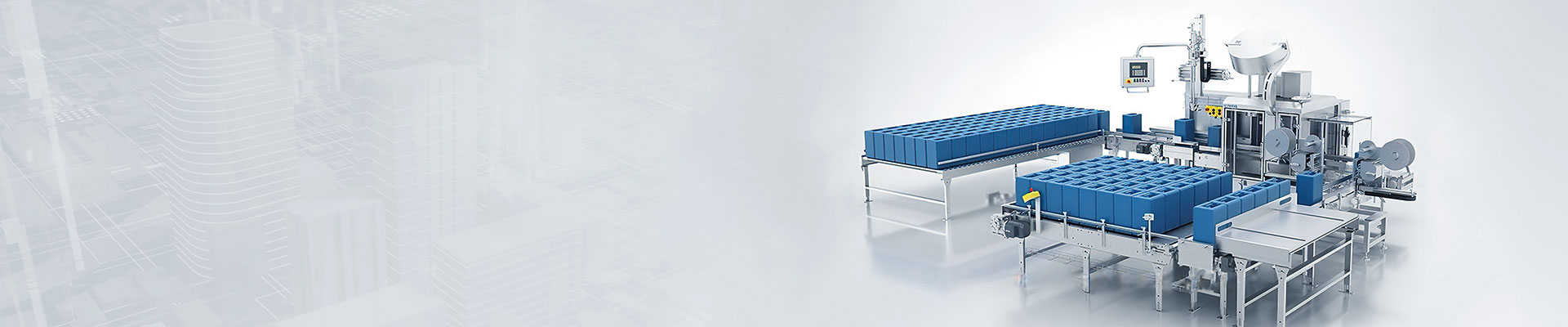
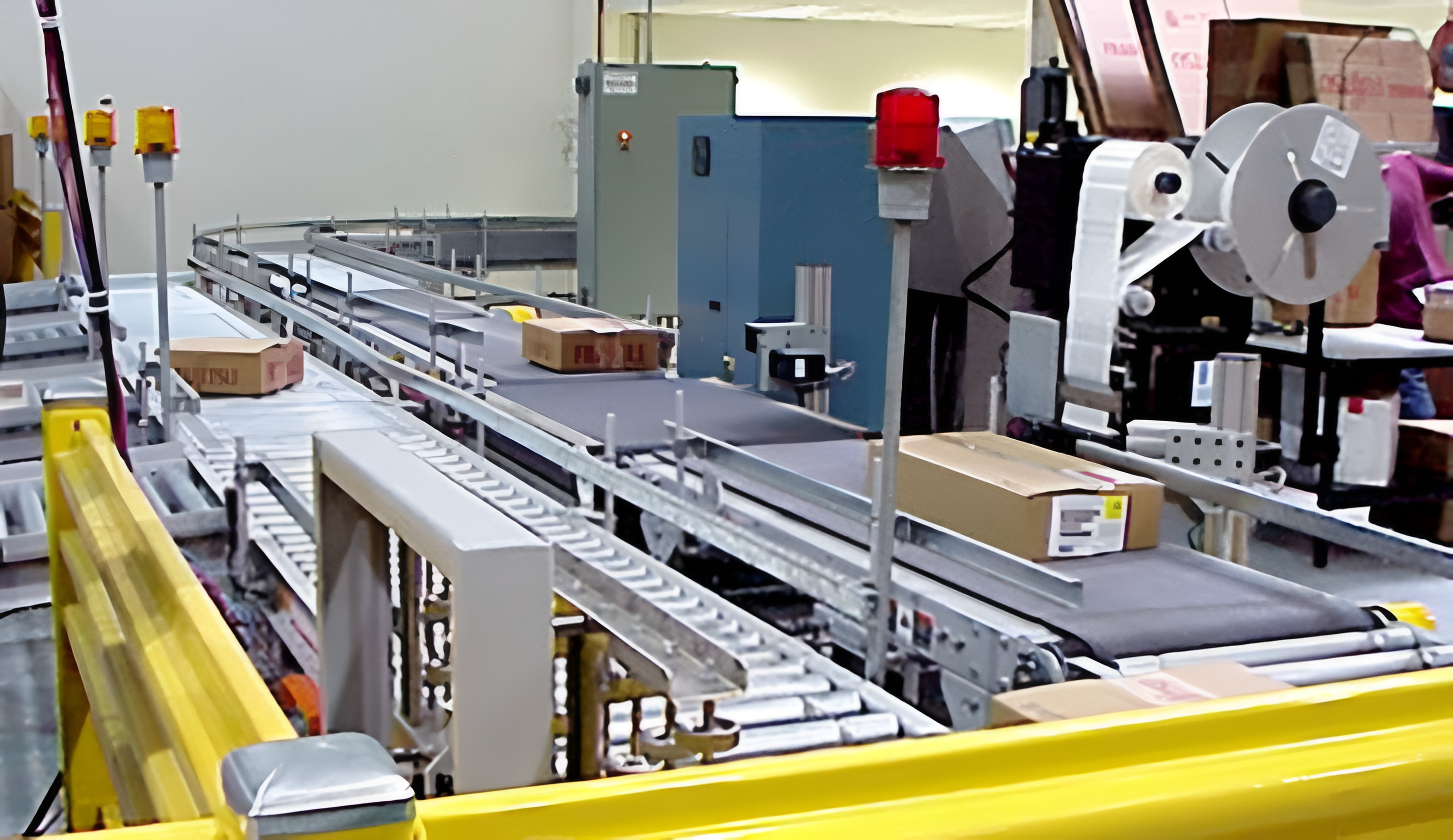
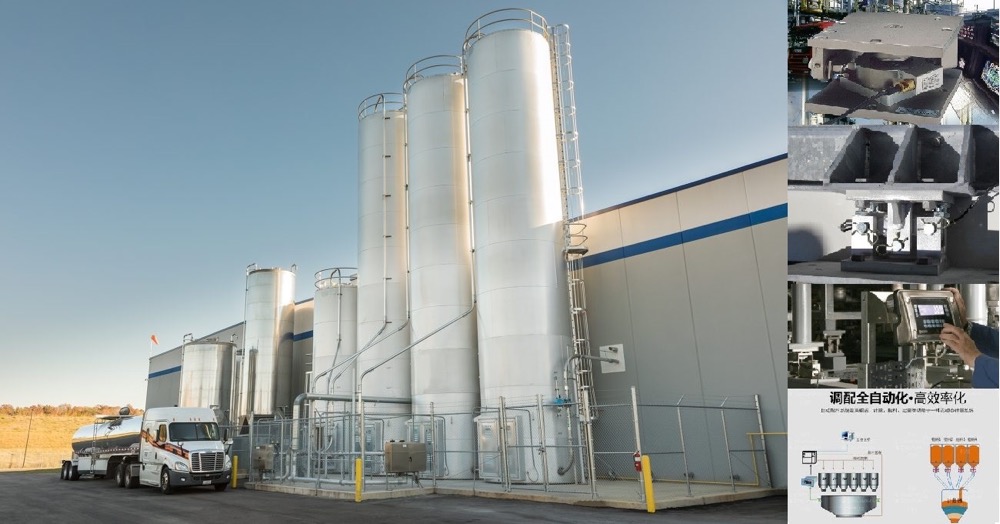
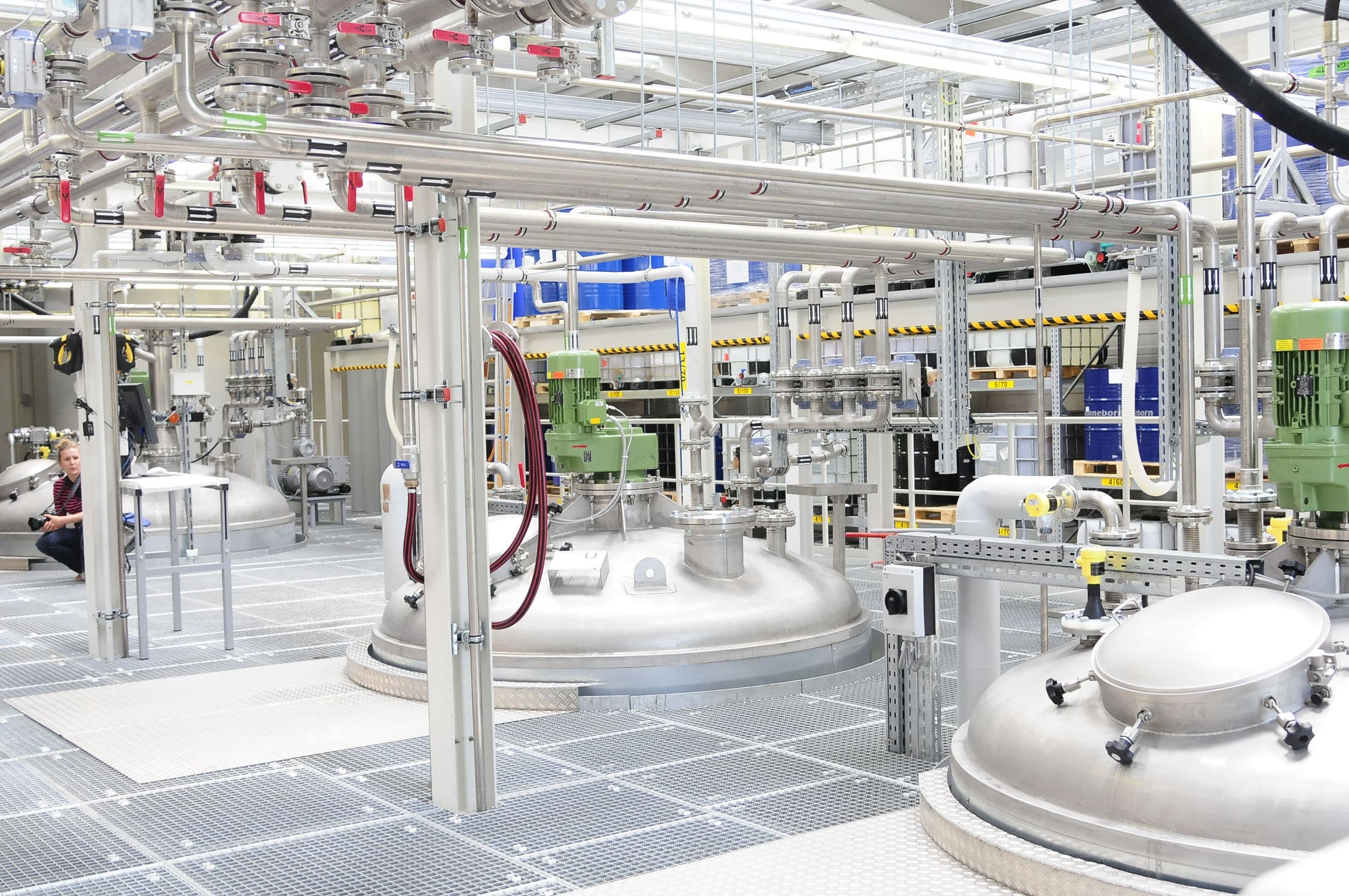
The blank sorting machine is composed of two parts: the flipping roller track and the non-conforming product conveying roller track. It enables the qualified and non-conforming products after sorting and inspection to be conveyed through different channels, thereby achieving the automatic separation of non-conforming products. The automated mechanical hand is used for the transportation of the blanks, the double-speed chain of the tooling board is used for the conveying of the blanks, and the automated three-dimensional warehouse serves as the storage unit for the blanks, which can realize the automation of the conveying and storage of the blanks after they are formed.
 020-34563445
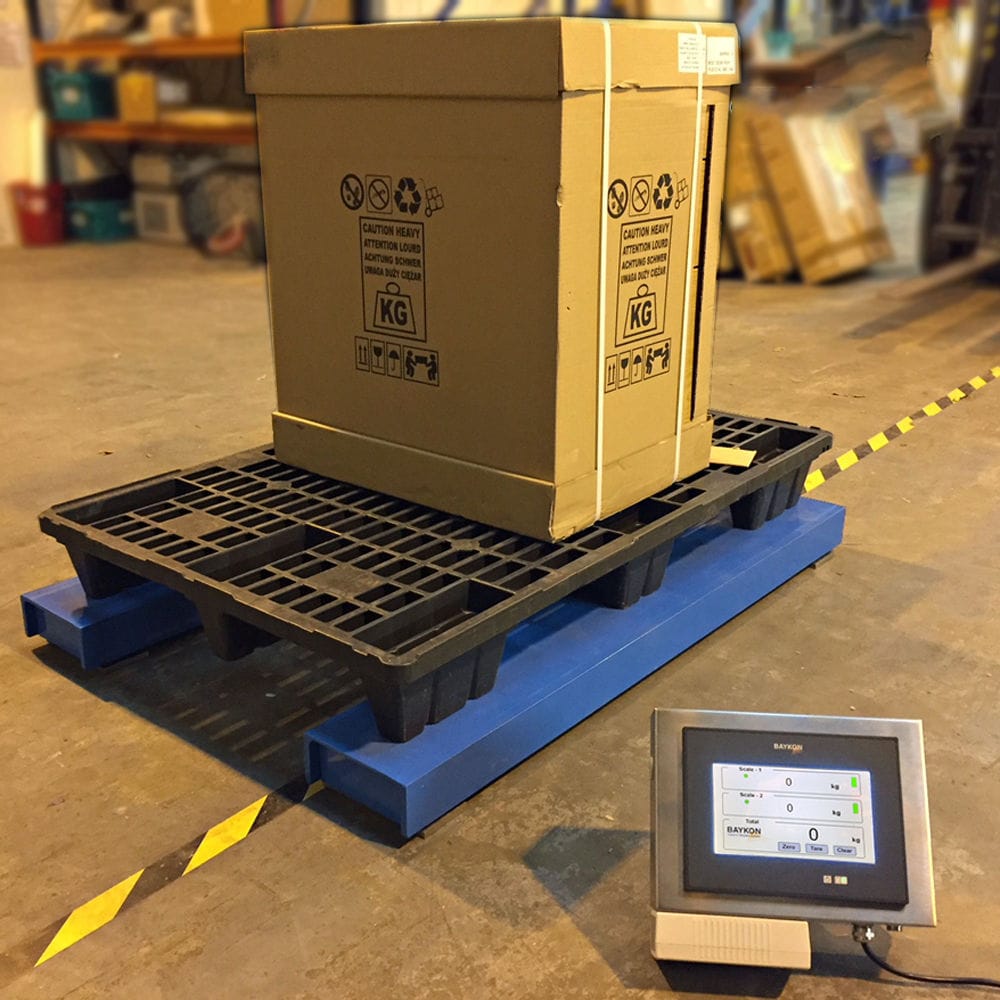
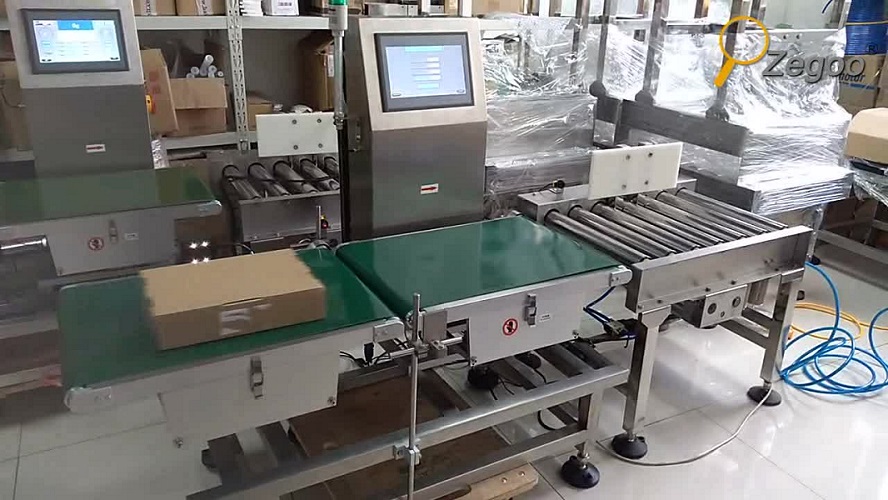
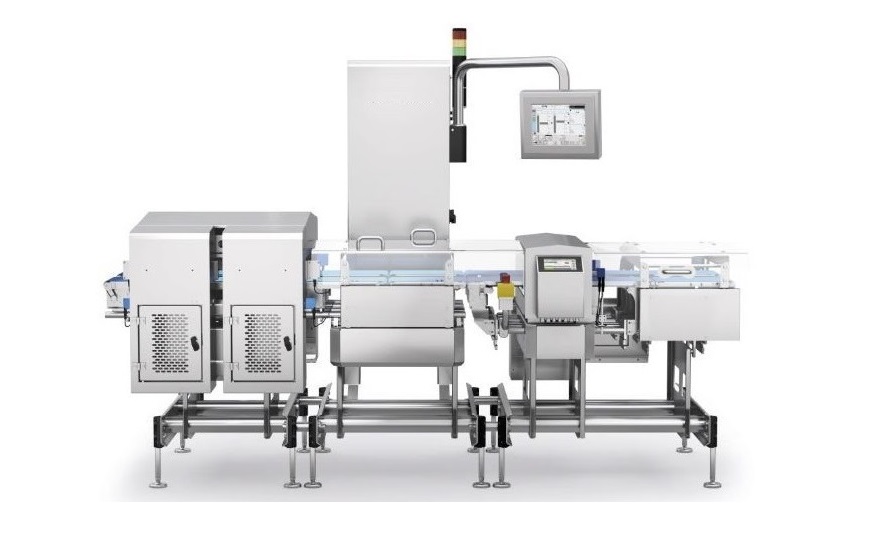
020-34563445The Weighing system of the Sorting machine realizes the automatic sorting operation of the blanks, and can collect and display real-time data such as quality information, record it into reports, and achieve functions such as monitoring, statistical query and printing, specification setting, report record traceability, specification selection, and statistical process control. Production transfer cards can be printed on site to provide support for product traceability.
The sorting machine is composed of two parts: the flipping roller track and the non-conforming product conveying roller track. It enables the qualified and non-conforming products after sorting and inspection to be conveyed through different channels, thereby achieving the automatic separation of non-conforming products. The sorting system for non-conforming products mainly operates in two ways: manual and automatic. When operated manually, the sorting device does not perform sorting. During automatic operation, qualified products are collected by the upper roller conveyor. When non-conforming products are detected, the PLC sends a signal, and the cylinder drives the sorting roller conveyor to flip, conveying the non-conforming products to the non-conforming product conveying roller conveyor. After the non-conforming products have completely passed through the sorting roller conveyor, the sorting roller conveyor rises to the initial position, and the non-conforming products are conveyed from the end of the lower roller conveyor and marked as invalid.
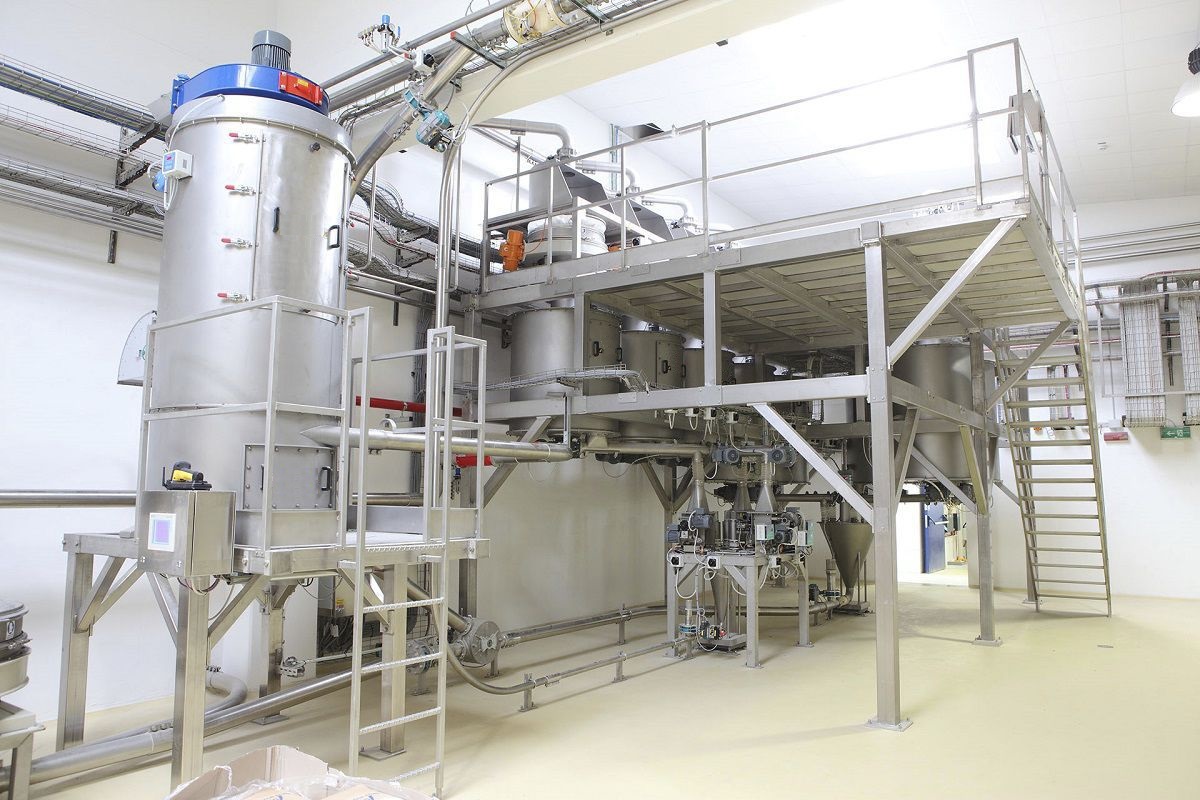
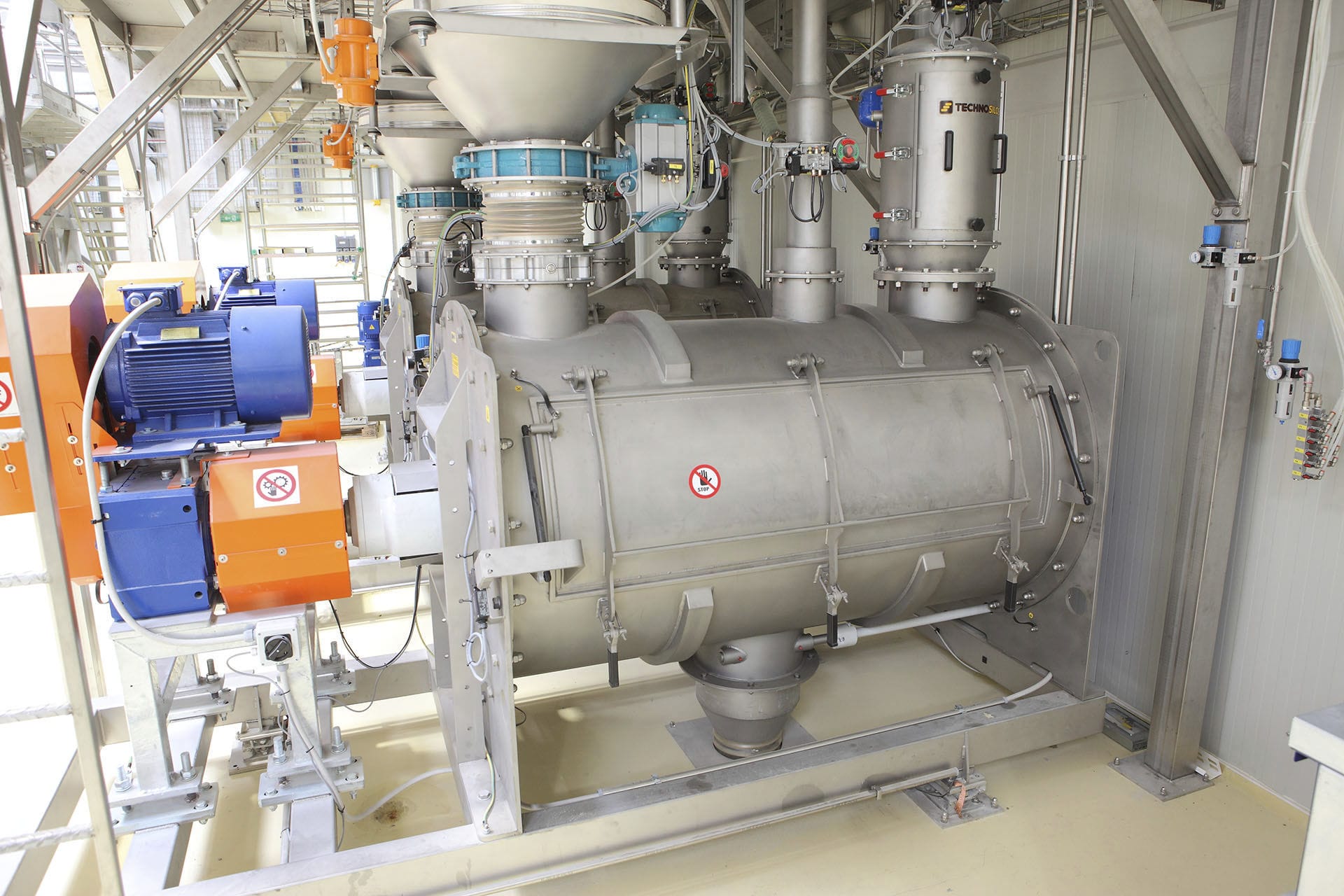
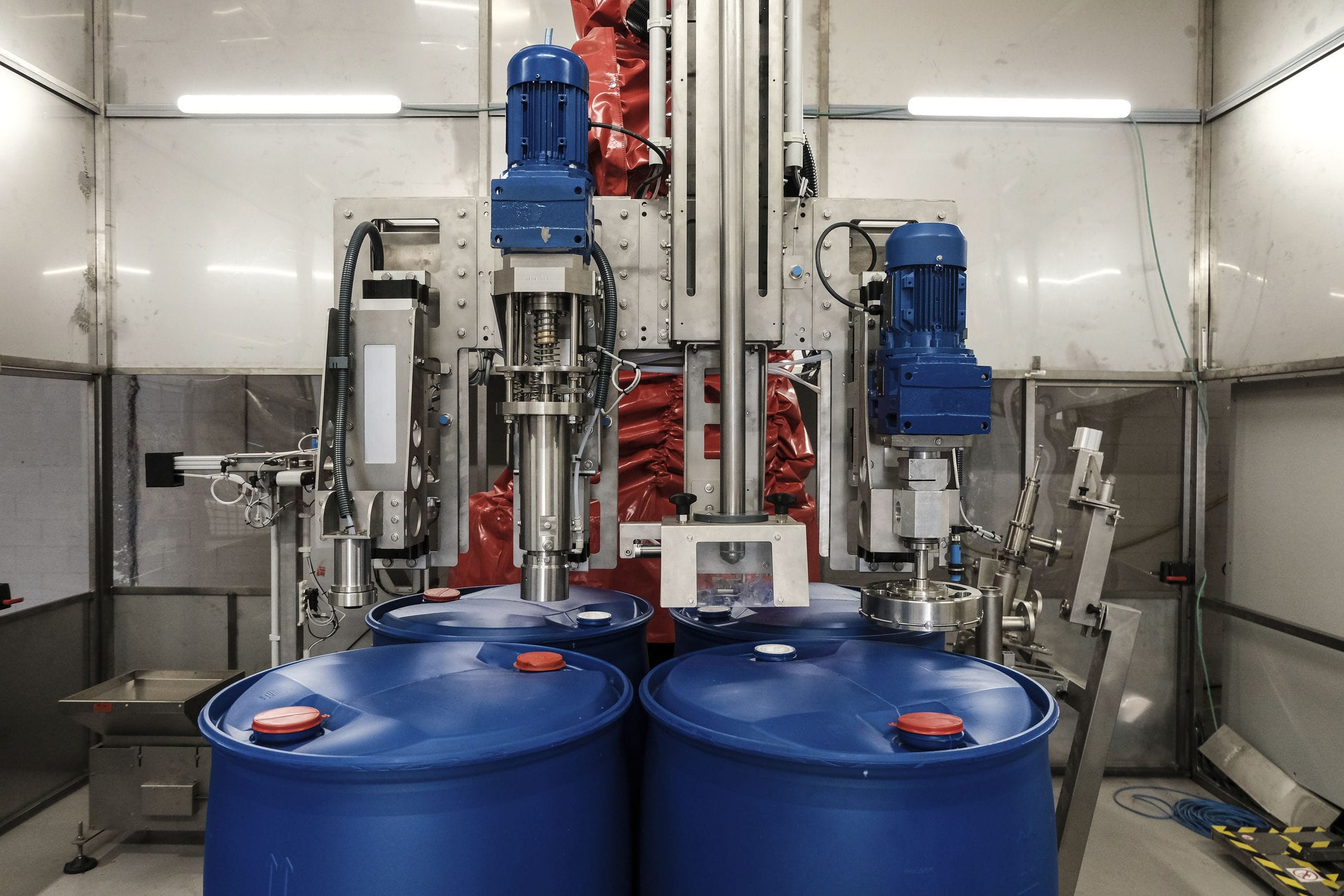
The weighing and sorting machine conveys the qualified quality blanks to the designated position. The handling manipulator operates and enters the forming machine to pick up the blanks. After the handling manipulator finishes picking up the blanks, it moves the blanks to the position of the blank flipping manipulator and places them inside. Then, the handling manipulator exits and waits for the next qualified weight blank to be formed. After the handling manipulator exits, the blank flipping manipulator operates, flipping the vertically placed blank to a horizontally placed one. At the same time, it moves to the position where the gantry manipulator grabs the blank, where the gantry manipulator picks up the blank and moves it into the double-speed chain of the tooling plate.
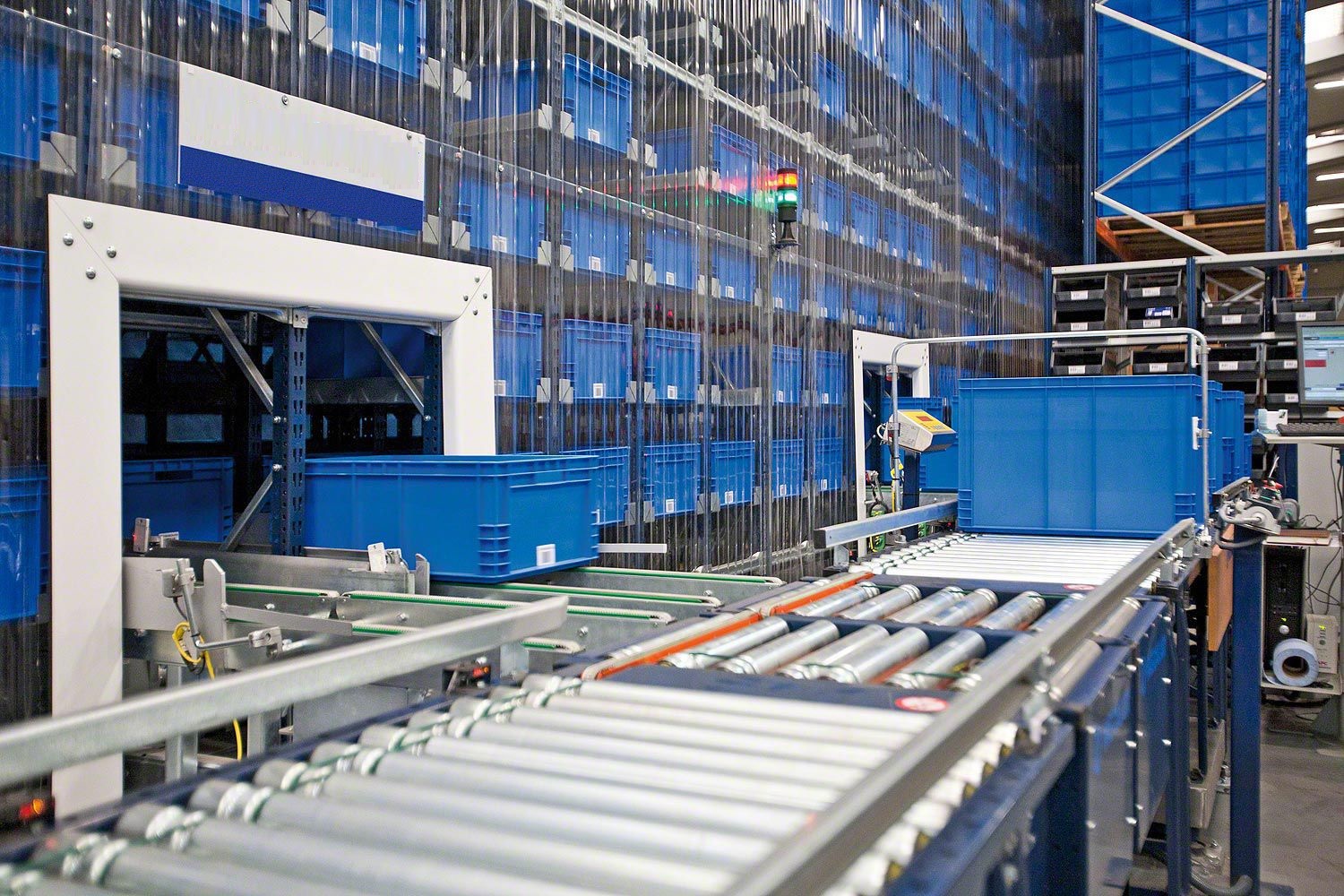
When the blanks are conveyed to the warehouse entrance through the double-speed chain of the tooling plate, the gantry manipulator in the warehouse grabs the blanks on the tooling plate and places them in the blank shelves of the tray assembly trolley. After the blanks are placed on both shelves of the tray assembly trolley, the truss manipulator moves them into the warehouse and simultaneously moves the blanks that need to be taken out of the warehouse into the tray assembly trolley for removal by the gantry manipulator. The empty tray is returned to the forming machine to complete one cycle. The blank shelves in the warehouse are made according to the shape of the blanks. After the blanks are placed in, it can ensure that the blanks do not deform or undergo minimal deformation.
In the transportation and storage of the formed blanks, automated mechanical hands are used for the handling of the blanks, the double-speed chain of the tooling plate is used for the transportation of the blanks, and the automated three-dimensional warehouse is used as the storage unit of the blanks. This can achieve the automation of the transportation and storage of the blanks after forming, as well as real-time monitoring, statistical query and printing, specification setting, report record traceability, specification selection and statistical process control functions. The data in the entire control system can be collected, analyzed and processed. The human-machine interface can display the current production status of the sorting scale in real time, including detailed parameters of the specifications currently in production, such as production quantity, quality, pass rate and trend curve, etc., to facilitate understanding of the current operation status of the equipment. The weighing system can display various data collected from the PLC in real time. The software presents the data collected by the PLC from the equipment in an aesthetically pleasing continuous line mode in real time, enabling operators to have a more intuitive and clear understanding of the status of the blank production line.