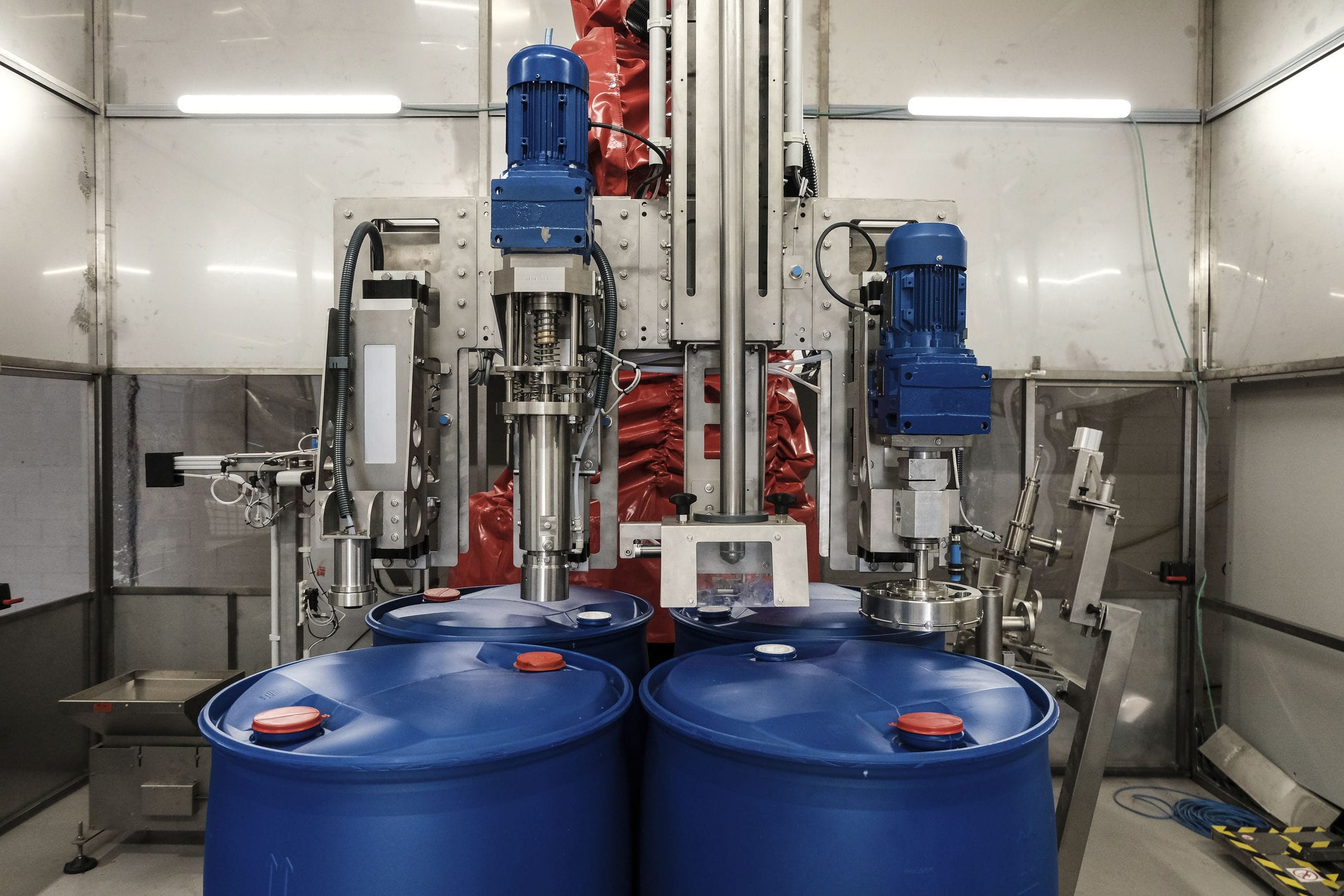
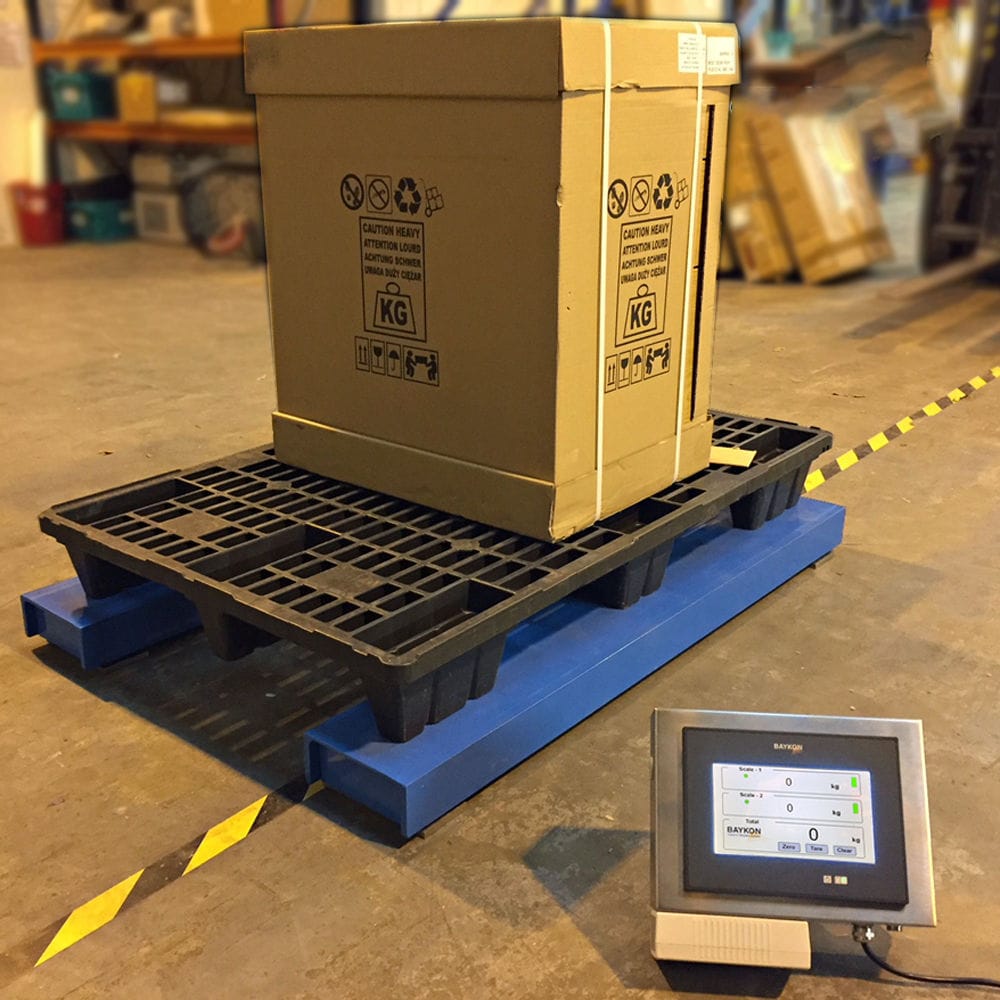
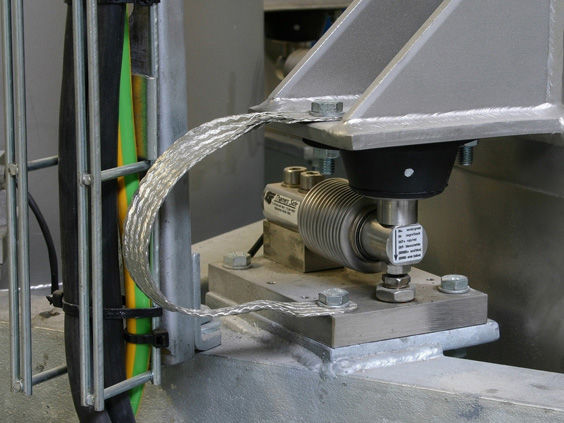
The photoelectric separator adopts the principle of electronic weighing. Within one data acquisition cycle, the weight of the drum is weighed first, then the weight of the drum plus the material is weighed. The actual weight of the material block is obtained by subtracting the two. When the sorting machine starts up, the electronic scale turns on, and the DC motor drives the drum to rotate. The discharge door closes, and the electronic scale displays the stable value in the no-load running state, that is, the weight of the drum. When the material block falls from the upper slide way, the switch responds, the discharge door opens, and the material block falls into the material trough of the drum. The reading on the electronic scale gradually stabilizes as the drum rotates, and the stable value after feeding is obtained, that is, the weight of the drum plus the material block.
 020-34563445
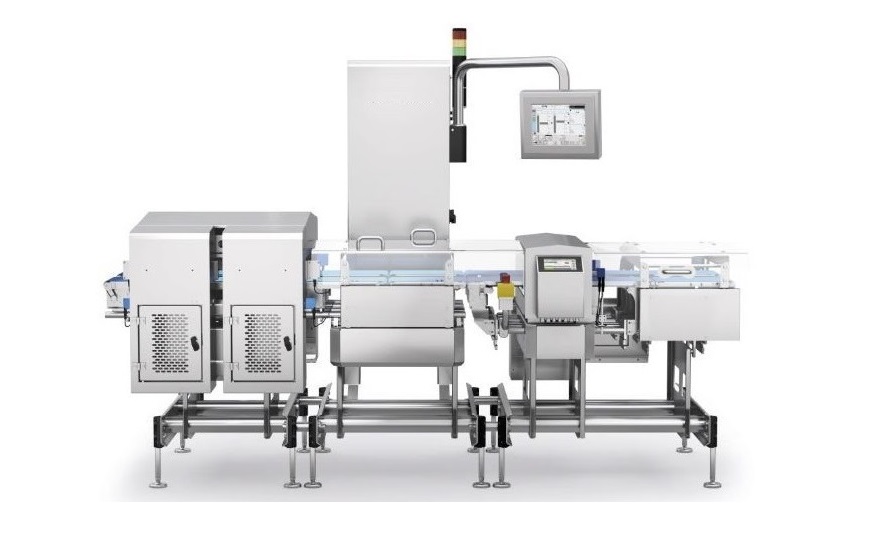
020-34563445The photoelectric Sorting machine is used in factories to sort and package different materials. Various sensors are used to distinguish different materials, and then the processing method of the materials is controlled by the PLC program. The materials that do not meet the requirements are transported to the material recycling tank. The conveying system can replace the repetitive and monotonous operations of humans and has outstanding advantages in ensuring product quality and achieving safe production.
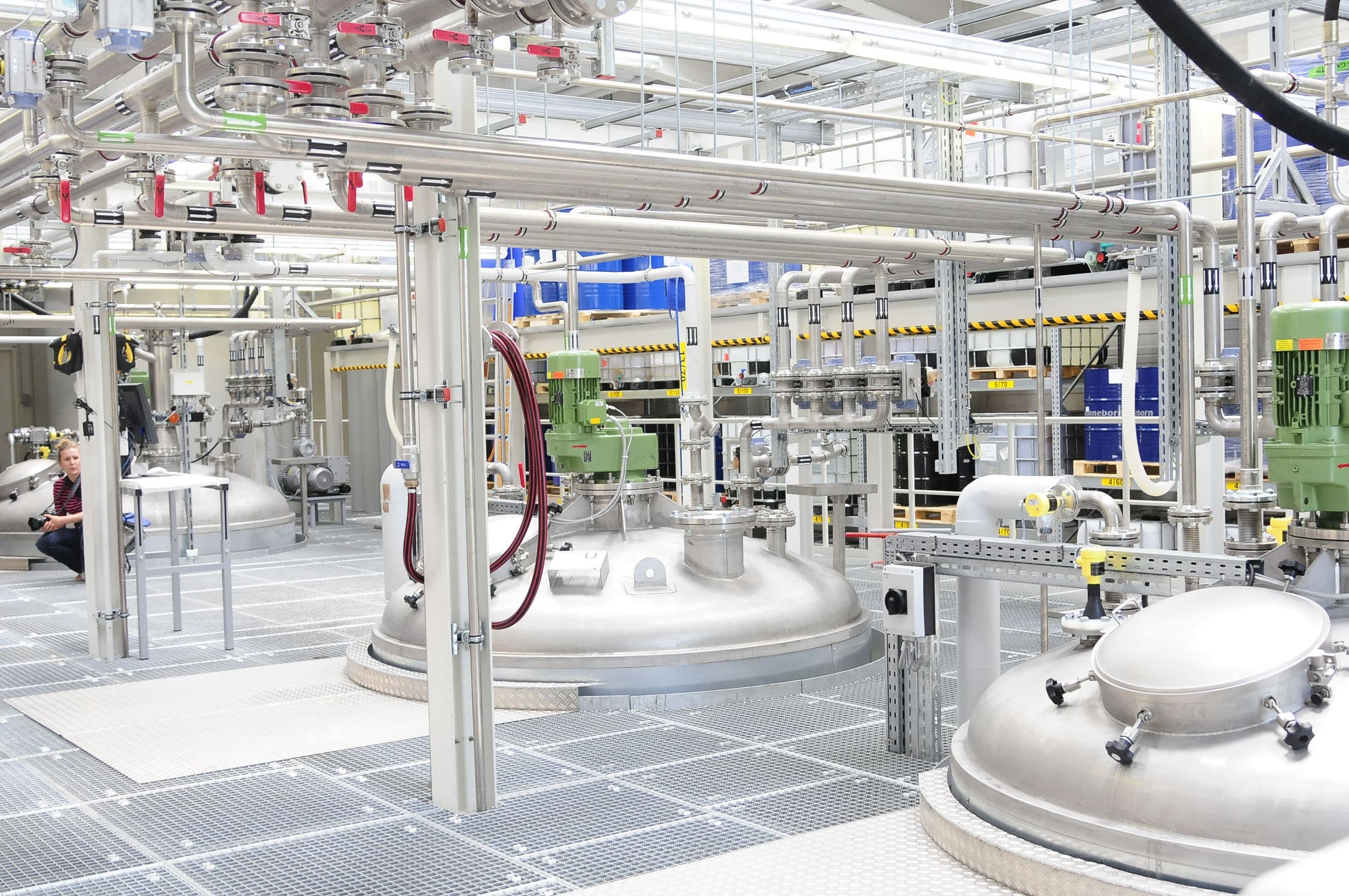
The sorting machine consists of a mechanical part and a control system. The mechanical part realizes feeding, weighing and sorting; the control system is implemented by PLC to control all the actions of the sorting machine, and the industrial control computer communicates with the Electronic scale and PLC through serial ports and data acquisition cards to collect and process measurement signals. The hardware of the sorting machine control system mainly consists of the electronic scale, industrial control computer, PLC, photoelectric switches, stepper motors and interface circuits.
The sorting machine adopts the differential weighing principle. Within one data acquisition cycle, the weight of the drum is measured first, then the weight of the drum + the material is measured, and the difference is obtained to obtain the actual weight of the material block. When the sorting machine starts, the electronic scale is turned on, the DC motor drives the drum to rotate, the discharge door is closed, the electronic scale shows the stable value in the idle state, which is the weight of the drum. The photoelectric switch responds when the material block falls from the upper slide track, the discharge door opens, the material block falls into the drum material slot, and the value displayed by the electronic scale gradually stabilizes during the rotation of the drum, obtaining the stable value after adding the material block, which is the weight of the drum + the material block.
According to the control requirements, PLC realizes the working process of the mechanical part, the electronic scale measures the weight of the drum and the material block, the data is transmitted to the industrial control computer through the RS-232C interface; the industrial control computer analyzes and processes the data to obtain the measurement value and compares it with the set value to obtain the grouping result, and the digital 0 card notifies the PLC of the grouping result, and the PLC transmits the material block to the designated storage bin according to the grouping result.
The drum continuously rotates and transports the material block through the slide track to the sorting device. The industrial control computer obtains the weight of the drum by sampling the electronic scale; the vibrating hopper and the linear conveyor work, the photoelectric switch detects the material block, the photoelectric switch opens the discharge door, the material block falls through the slide track into the drum material slot, the electronic scale's value gradually stabilizes during the rotation of the drum, obtaining the stable value after adding the material block, which is the weight of the drum + the material block. The drum rotates and transports the material block through the slide track to the sorting synchronous belt, the processing result is notified to the PLC by the industrial control computer, the PLC starts the stepper motor, drives the synchronous belt to forward transport the material block, reaching the predetermined storage bin, the PLC starts the electromagnetic valve to trigger the signal, the conveyor works, the material falls into the storage bin.
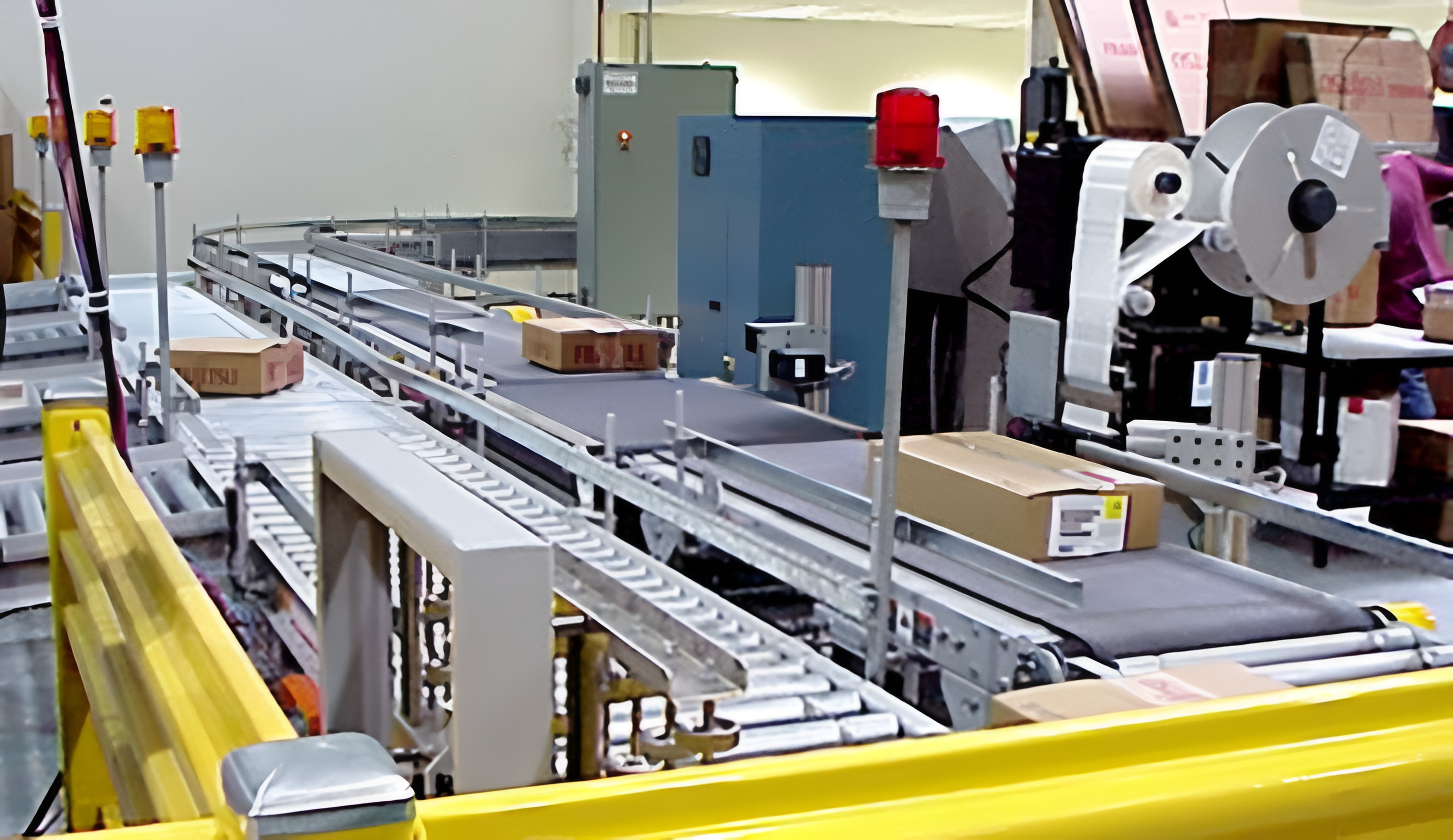
The main function of the sorting machine is to transport the materials from the feed inlet to the corresponding position for processing, mainly consisting of belt conveyors and three-phase asynchronous motors. The motor drives the main shaft of the conveyor to rotate, the friction between the conveyor belt and the main shaft drives the conveyor belt to move, relying on the friction force between the conveyor belt and the materials, the materials can move in the same direction as the conveyor.
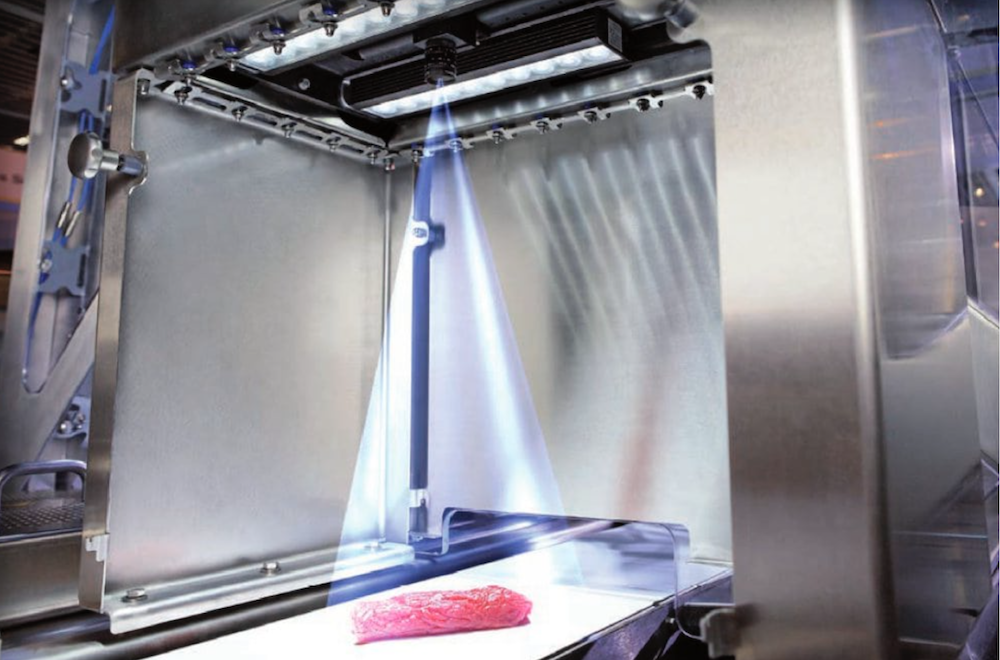
The sorting machine mainly consists of solenoid valves, air compressors, cylinders, stepper motors, rotary encoders, sensors and conveyor belts. On the upper part of the recycling tank of the sorting machine, there is a photoelectric detection sensor for detecting whether there is material in the material slot, sensors of inductance, capacitance and color are installed above the conveyor belt respectively for detecting materials and non-metallic materials, and the spare sensor at the end of the conveyor belt can be selected as a color sensor or photoelectric sensor for detecting other materials. The conveyor belt is driven by the stepper motor for material transportation. The shaft of the stepper motor is connected coaxially with the rotary encoder, every time the encoder rotates one circle, it outputs several pulse signals to the PLC, the PLC controller can determine the number of rotations of the stepper motor according to the number of input pulses, thereby calculating the horizontal moving distance of the material on the conveyor belt. It is mainly composed of various sensors and the piston rods of the material pushing cylinders. There is a material photoelectric detection sensor at the feed inlet, which mainly functions to detect whether any material has entered the feed inlet. Additionally, in front of the feed inlet, there are an inductive sensor and a fiber optic sensor. The inductive sensor is used to detect metallic materials, while the fiber optic sensor is used to detect white materials. The sensitivity of these two sensors can be adjusted. Before the system operates, the sensitivity is manually adjusted to meet the above requirements.
After the material enters the feed inlet, the motor drives the belt to rotate and forwardly convey the material. During the forward movement of the material, the photoelectric sensors at the feed inlet, the inductive sensor, and the fiber optic sensor distinguish the type of the material. When the material is metallic, the inductive sensor outputs a switch signal; when white plastic passes through, the fiber optic sensor also outputs a switch signal; while for black materials, these two sensors do not act, thereby distinguishing the three types of materials. The data registers of PLC are used to record the number of metallic materials, white plastic, and black plastic respectively. As soon as the corresponding workpiece passes, the corresponding data register is activated. Then, the system processes based on the number of times the material is pushed into the material slot. When the material is pushed into the material slot, the system pauses for half a minute to package the material. If the materials do not meet the requirements, they are clamped back into the recycling tray by the conveyor. When all the slots have completed sorting, the system stops for 30 seconds to package the materials, and then continues to work in a cycle. When the materials do not meet the packaging requirements, the first three cylinders will not act. The material continues to move forward until it is detected by the fiber optic sensor. At this point, the motor stops running, and the conveyor operates according to the sequence of extending the cylinder > lowering the hydraulic clamp > clamping the workpiece > rising the hydraulic clamp > retracting the cylinder > turning the conveyor to the right > extending the cylinder > lowering the hydraulic clamp > releasing the fixture > rising the hydraulic clamp > retracting the cylinder > turning the conveyor to the left. After the conveyor clamps the workpiece, the motor immediately runs at a low speed. When the photoelectric sensor at the material inlet detects the next material, the motor runs at a high speed.